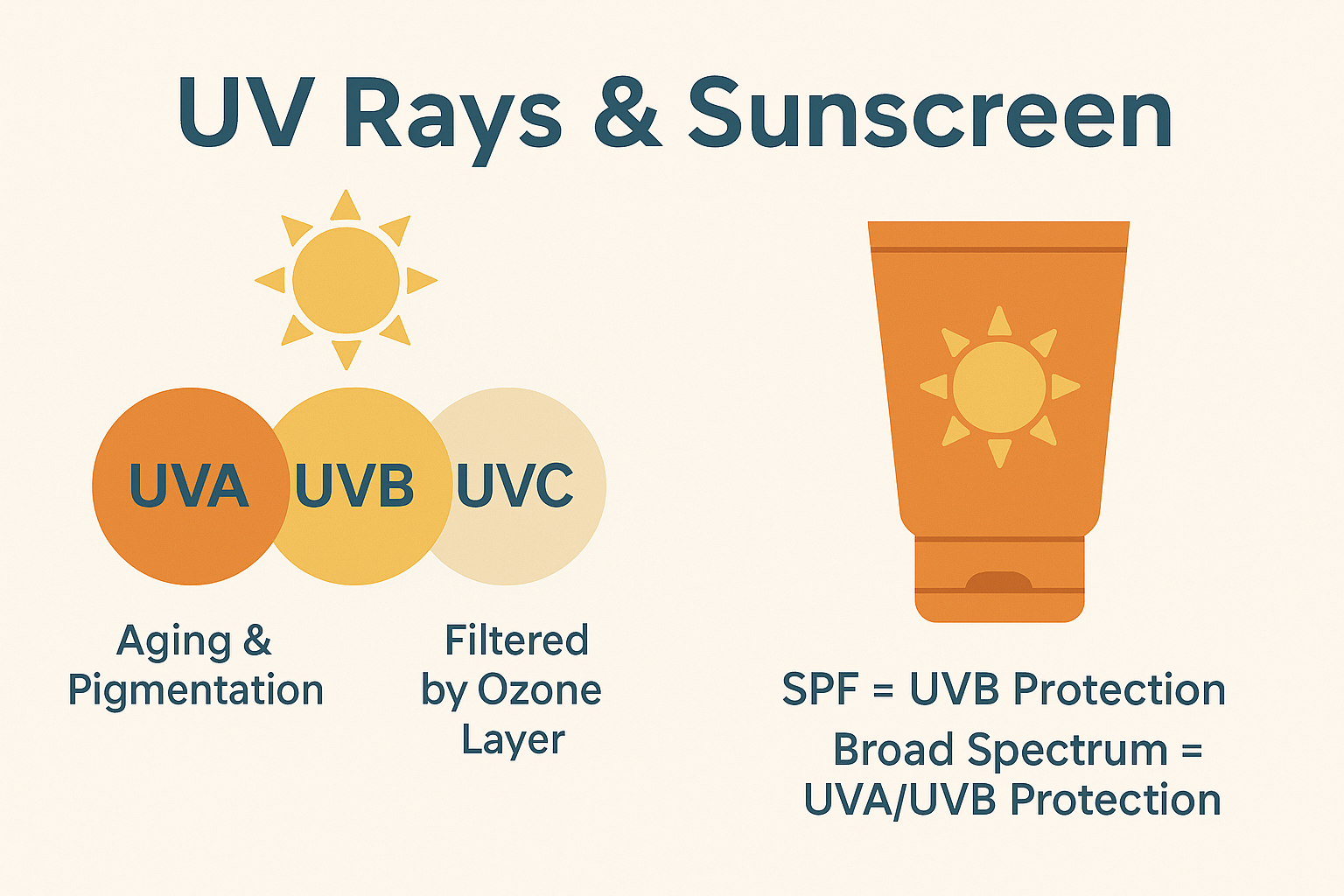
UVA, UVB, and UVC Rays – Their Impact on Your Skin
When we talk about sun damage, not all ultraviolet (UV) rays are created equal. Here’s what each type does:
Types of UV Radiation:
- UVA (320–400 nm):
- Penetrates deep into the dermis.
- Causes tanning, pigmentation, and premature aging (wrinkles, loss of elasticity).
- Main culprit behind melasma, hyperpigmentation, and long-term skin damage.
- UVB (290–320 nm):
- Affects the epidermis (top skin layer).
- Leads to sunburn, redness, and temporary tanning.
- Plays a major role in skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma.
- UVC (100–290 nm):
- Mostly absorbed by the ozone layer.
- Does not reach the Earth’s surface.
How Sunscreen Protects You
🧴 SPF – Sun Protection Factor
- Measures protection against UVB rays (burning).
- SPF 30 blocks ~97% of UVB, SPF 50 blocks ~98%.
🌫️ PA Rating – Protection Grade of UVA
- Measures protection against UVA rays (aging & pigmentation).
- PA+ (some protection) to PA++++ (highest protection).
☑️ Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen
- Protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Essential for preventing both sunburn and long-term skin issues.
Sunscreen Recommendations
For Indian Skin:
- Choose SPF 30–50, PA+++ or higher.
- Opt for gel-based or matte-finish for oily/acne-prone skin.
- Look for zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or avobenzone as active ingredients.
For Global Use:
- Dry Skin: Go for cream-based sunscreens with added moisturizers.
- Oily Skin: Use non-comedogenic, gel-based, or mineral sunscreens.
- Sensitive Skin: Mineral sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide work best.
Quick Recap
- UVA = Aging, Pigmentation, Tanning
- UVB = Burning, Redness, Temporary Tanning
- UVC = Not a concern for the skin
Pigmentation and tanning are primarily caused by UVA rays, which deeply stimulate melanin production. UVB contributes, but mostly results in burning and superficial tanning.
Always choose broad-spectrum sunscreens to ensure full protection.